PandaDoc Review: Features, Pricing, Integrations, Pros/Cons, and Best Alternatives
If you’ve ever watched a deal stall because “the proposal is in someone’s inbox,” you already understand the real problem PandaDoc is trying to solve. Most teams don’t struggle because they can’t create documents. They struggle because proposals, quotes, contracts, and approvals are scattered across tools, threads, file versions, and handoffs—so execution becomes slow, error‑prone, and impossible to measure.
PandaDoc positions itself as a full agreement workflow platform: create and generate documents, configure quotes, collaborate (including negotiations/redlining), collect legally valid e‑signatures, accept payments, and track engagement—all in one system. It’s built for revenue teams, customer success, operations, and legal stakeholders who want a repeatable “from draft to signed (and paid)” pipeline, not just a signature tool.
Overall verdict: 8.8/10
PandaDoc is one of the strongest options if you need document creation + quoting + workflow controls + analytics in one place. The trade‑offs are that advanced capabilities (CPQ, deeper workflow automation, certain compliance flows like QES credits) can add cost/complexity, and teams that only need simple eSign may find it more than they require.
PandaDoc
PandaDoc is a great addition to any business with its many features and flexibility. PandaDoc is basically a web-based application that allows users to create, deliver, and share documents online and place their legally binding signatures for faster paperless transactions and processes. The system supports various document forms including PDFs, Docs, and other pre-existing digital documents. It works well with quotes, contracts, agreements, and other sales collateral. There has been a 15% increase in average contract value with PandaDoc, one hour saved per week per employee and a 10% increase in close rate. PandaDoc is the future of document managing.…
Here’s what this review covers
- Overview and company background
- Pricing and plans (with comparison table + hidden costs)
- Setup and onboarding experience
- UI, usability, and learning curve (with screenshot checklist)
- Core features breakdown
- Advanced features and integrations
- Performance, reliability, and security
- Customer support and resources
- Pros and cons
- User reviews and ratings summary
- Alternatives and comparisons
- Who it’s best for (and who should avoid it)
- Final verdict and recommendations
- FAQ (15 common questions)
Overview and Company Background
What PandaDoc is
At its core, PandaDoc is an agreement management platform designed to standardize how organizations generate, send, negotiate, sign, and track business documents. The product scope spans:
- Document generation (templates, variables, content reuse)
- eSignatures (legally binding signature requests, audit artifacts)
- Tracking & analytics (page-by-page engagement and audit history)
- Payments (collect payment through connected processors, depending on configuration)
- CPQ (configure/price/quote workflow, CRM-connected)
- Deal rooms (“Rooms”) to consolidate stakeholders and assets in a shared space
- Workflow automation + approvals for operational control at scale
- Developer APIs + embedding for product-led and platform-led deployments
PandaDoc reports adoption at a scale of ~68,000+ customers across multiple product pages and feature modules, which aligns with its positioning in mid-market and enterprise segments.
Who it’s for (in plain terms)
PandaDoc is best understood as a fit for teams that:
- ship high volumes of proposals, quotes, or contracts, and want a consistent workflow
- want to reduce manual errors (pricing logic, versioning, missing fields)
- care about buyer experience (interactive docs, guided quoting, embedded payments)
- need approvals, roles/permissions, auditability, and measurable document engagement
If you’re a solo operator or a small team who only needs “send PDF → get signature,” PandaDoc can still work (there’s even a free tier), but you may not use enough of the platform to justify the steeper plans.
PandaDocMarket positioning and differentiators
PandaDoc competes in a crowded space that includes signature-first tools (DocuSign, Dropbox Sign) and proposal-first tools (Proposify). Its differentiation is that it tries to unify:
- content + creation,
- quote configuration,
- collaboration + approvals,
- signature + compliance, and
- tracking + automation,
within one operational model.
Key differentiators at a high level:
- Document generation at scale (batch creation, triggers, and developer-led automation)
- CPQ integrated into doc flow (rules-based pricing, approvals, CRM sync)
- Deal rooms (Rooms) as a closing environment, not just a document link
- AI contract assistant baked into workflow concepts (summaries, Q&A, email drafting)
- Embedded signing and API tooling for platform integrations and product embedding
Pricing and Plans
PandaDoc offers:
- a free eSign plan (useful for low volume signature workflows),
- paid tiers for growing teams, and
- an enterprise tier for advanced workflows, integrations, and governance.
It also promotes a 14‑day free trial flow for paid evaluation.
Plan-by-plan breakdown (what matters in practice)
Free eSign (Free)
This tier is best thought of as a “proof of value” plan:
- $0
- Unlimited seats
- 60 documents per year (the real limiting factor)
- Includes basic signature requests and audit trail basics, plus support availability noted on the pricing page
Who it fits: founders, freelancers, or internal teams that sign infrequently and don’t need templates, catalog/pricing logic, approvals, or CRM sync.
Who will outgrow it quickly: any sales org sending more than a few proposals a week.
Starter
Starter is where PandaDoc begins to shift from “signing tool” to “document workflow tool,” with pricing shown as:
- $19 per seat/month billed annually
- $35 per seat/month billed monthly
Typical fit: small sales teams that need consistent proposals, basic brand control, and tracking—without heavy operational governance.
Business
Business is positioned for teams that need collaboration at scale and deeper process controls, priced at:
- $49 per seat/month billed annually
- $65 per seat/month billed monthly
Where Business tends to win is when you need shared assets (content library), pricing tables/catalog use, approval flows, and more structured workflows. (Notably, PandaDoc’s own help-center materials indicate certain quote tooling such as pricing tables map to Business/Enterprise availability.)
Enterprise (Custom)
Enterprise is “contact sales,” typically for:
- SSO/security requirements
- multi-team governance
- advanced automation and CPQ needs
- API/embedded deployments at scale
Pricing comparison table
| Plan | Price (Annual billing) | Price (Monthly billing) | Key limits | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free eSign | $0 | $0 | 60 docs/year (primary constraint), unlimited seats | Low-volume signing, testing the workflow |
| Starter | $19/seat/mo | $35/seat/mo | Scales beyond free; designed for small teams | Small sales teams that want branded proposals + basic tracking |
| Business | $49/seat/mo | $65/seat/mo | Built for collaboration + controls | Teams needing templates + shared assets + approvals + quoting tooling |
| Enterprise | Custom | Custom | Contracted | Org-wide governance, SSO, advanced workflows, embedded/API needs |
Hidden costs and add-ons to watch
PandaDoc is relatively transparent on core seat pricing, but “real world cost” often comes from compliance and workflow extras.
PandaDoc- QES (Qualified Electronic Signature) credits
If you operate in EU contexts requiring the highest eIDAS signature level, PandaDoc’s help center describes a credit model:- Available on Business and Enterprise
- $5 per unique signer = 1 QES credit (regardless of how many signatures they add to the document)
This is a classic “hidden cost” if legal/compliance teams later mandate QES for certain agreements.
- CPQ and advanced workflows
CPQ is a major capability—rules, approvals, CRM sync—but it’s also a “platform-within-a-platform.” If you don’t truly need configure/price/quote complexity, it’s easy to pay (in process complexity if not always in list price) for more than you use. - Data residency choices can require operational duplication
PandaDoc offers US and EU data center regions, but notes you can’t transfer data from one data center to another, and you may need a separate account for each region. That can translate into administrative overhead (and potentially duplicated licenses, depending on your org’s structure). - Premium support and services
The PandaDoc ecosystem includes onboarding services, professional services, and premium support options listed in the features/navigation resources. These are typically valuable for enterprise rollouts, but they’re also cost centers to plan for.
Value for money analysis
- Best value for most teams: Business, because it’s usually where workflow controls (approvals, shared assets, quote tooling) start matching real operational needs.
- Best for budget: Free eSign, but only if 60 documents/year is realistic.
- Best for scale and technical integration: Enterprise, especially when embedding or API-driven flows matter.
Setup and Onboarding Experience
Initial setup: what’s typically fast vs. what takes time
Most teams can stand up a basic PandaDoc workflow quickly:
- Create a template
- Add variables/fields
- Configure signing order
- Send a document, track engagement, and collect a signature
Where onboarding becomes “a project” is when you pursue:
- CRM mapping (opportunities, contacts, line items)
- product catalog buildout and pricing rules
- approval routing by deal thresholds
- workspace governance and role models
- embedding/API-driven generation
Guidance and learning resources
PandaDoc promotes:
- a Help Center
- webinars and templates resources
- a Learning academy
- structured onboarding services and professional services
This is a strong signal that PandaDoc expects both self-serve adoption (SMB/mid-market) and assisted deployments (enterprise).
Time-to-value: realistic expectations
A practical benchmark:
- Day 1–2: send branded docs from templates (basic value)
- Week 1: standardize your top 3–5 templates and implement tracking/audit conventions
- Weeks 2–4: CRM integration + basic catalog/pricing tables and approvals (meaningful operational value)
- Month 1–2+: CPQ rules engine, workflow automations, and embedded/API (platform-level value)
User Interface and Ease of Use
UI philosophy: document-first, workflow-second
PandaDoc’s UX is built around a familiar model:
- editor and template building for content teams
- send flows for sales reps
- tracking dashboards and audit views for managers, ops, and legal
The “drag-and-drop editor” is a key usability element. PandaDoc explicitly positions it as a modern alternative to the Word → PDF → eSign toolchain many orgs still use.
PandaDocLearning curve: who ramps fastest
Fastest ramp:
- sales reps using pre-approved templates and sending signature requests
- teams primarily using documents as a closing vehicle (proposals/contracts)
Moderate ramp:
- marketing and enablement teams building reusable blocks, themes, and content libraries
Steepest ramp:
- RevOps implementing CPQ rules, catalogs, approvals, CRM sync, and workflow automations in a governed way
Mobile experience (what you can reasonably assume)
PandaDoc’s signature flows are designed to work from “a computer or mobile device,” which matters because many agreements get signed on phones.
Operationally, PandaDoc also tracks “mobile application” status as a dedicated component on its public status page—indicating it maintains a first-party mobile surface.
That said, not all admin or configuration actions are mobile-friendly. For example, PandaDoc’s help center notes catalog items can’t be added using PandaDoc’s mobile app, which implies that mobile is optimized for execution (view/sign) more than configuration.
Customization options (what’s actually useful)
Customization isn’t about themes for aesthetics—it’s about governance and speed:
- brand styles and themes to prevent layout drift
- content locking to protect sensitive or legally approved sections
- team workspaces to separate departments/clients with roles and permissions
Core Features Breakdown
1) Document generation
Document generation is PandaDoc’s “engine room.” The platform highlights:
- creating documents from templates
- pulling data from systems (e.g., CRM)
- generating documents in response to business events
- batch generation of high volume documents
- embedding document creation inside other applications
Where this matters in the real world:
If your team sends 100 proposals a week, you don’t need “a better editor.” You need a controlled system where:
- pricing tables are consistent
- legal language is locked
- variables fill automatically
- approvals happen before the customer sees the document
- every doc is trackable
Practical workflow example (replicable)
- Ops builds a template with variables (company name, term length, SKU bundle)
- Template includes a pricing table and required signature blocks
- Rep generates a new doc from CRM context (or from a prefilled form)
- If discount threshold is exceeded, the doc routes to finance approval
- Once approved, the doc is sent; engagement is tracked automatically
2) Drag-and-drop editor
PandaDoc explicitly positions its block-based editor as a productivity upgrade compared to the traditional Word/PDF workflow. That’s not just marketing: it’s how you make templates maintainable when multiple teams contribute.
Strengths
- structured layouts reduce “template drift”
- easier reuse of blocks and sections (especially with content library)
Potential weakness
- some teams prefer Word-native editing for heavily negotiated legal documents (though PandaDoc supports negotiation workflows like redlining)
3) eSignature requests + signing workflows
PandaDoc supports digital signature requests as a core capability, emphasizing legally binding signatures and mobile-friendly signing.
Key operational elements
- signing order rules (who signs when)
- ID verification options and signer validation (important for higher-trust workflows)
- signature certificates (downloaded documents include a certificate artifact)
Why this matters:
Modern signature tooling is table stakes. The differentiator is how signatures connect to the broader workflow: template governance, audit history, integrations, and automation.
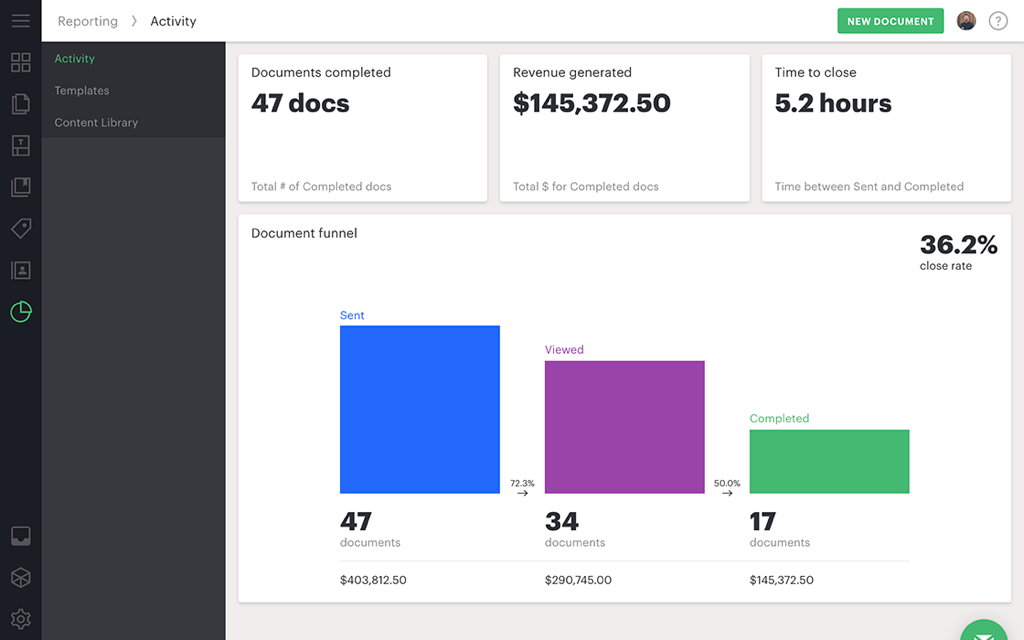
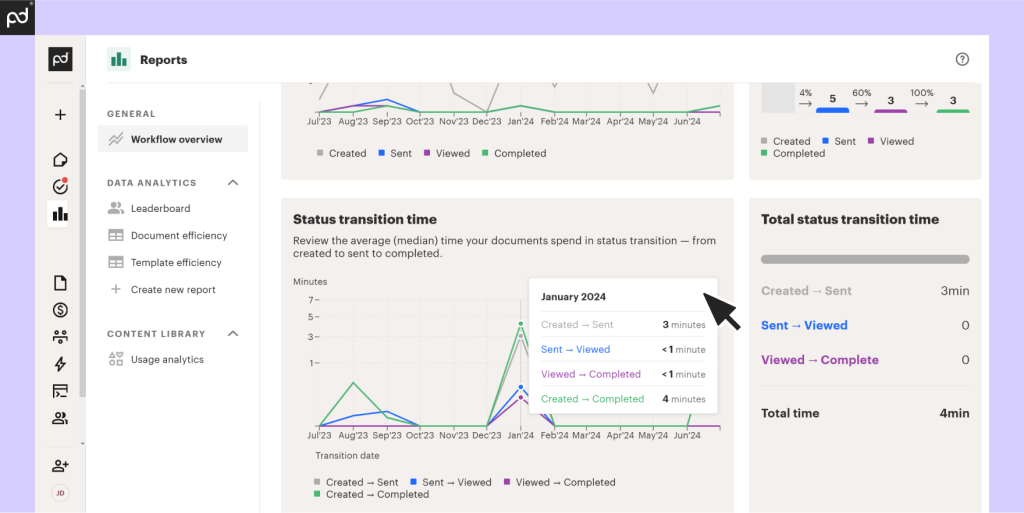
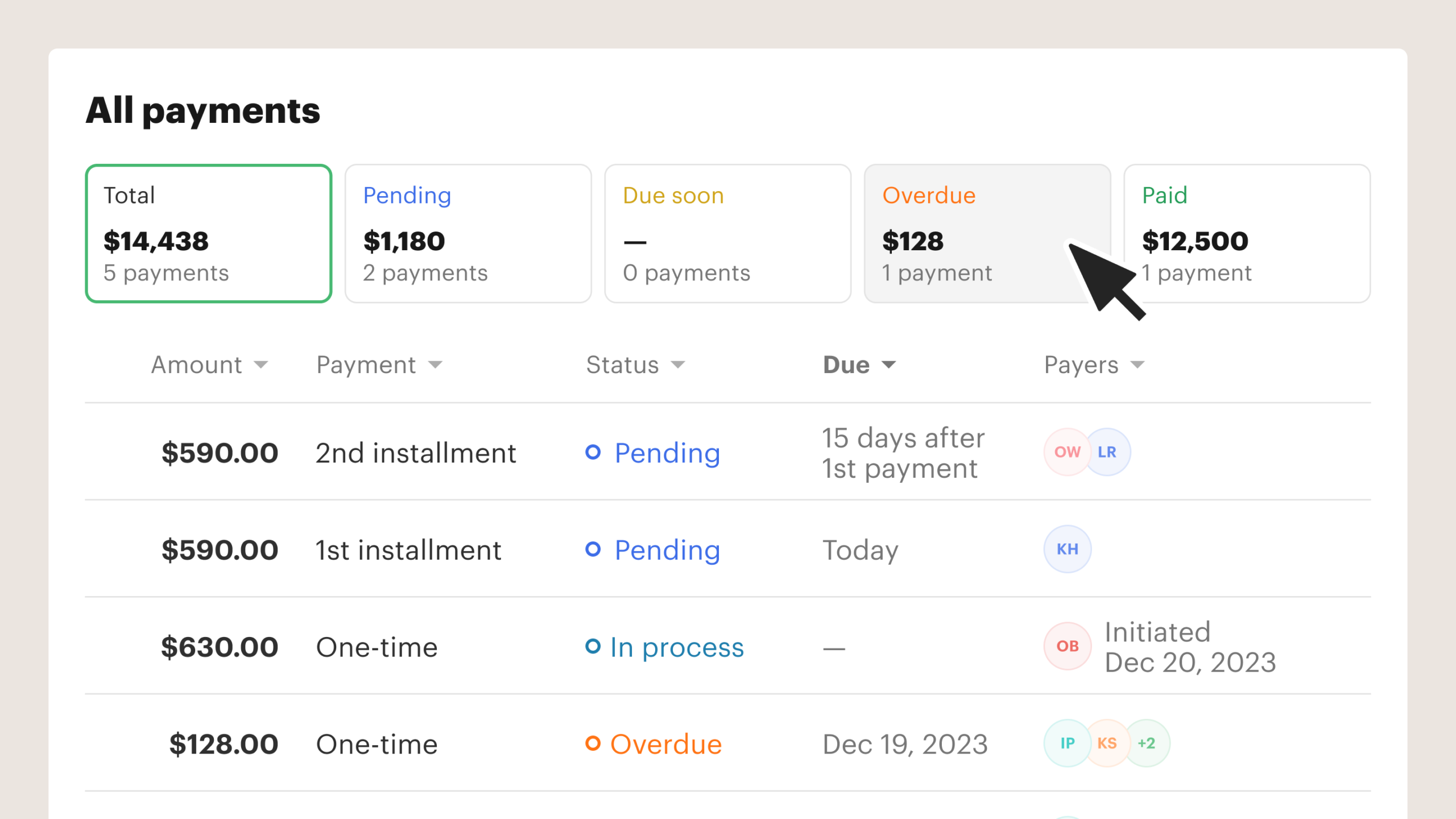
4) Document tracking, analytics, and audit history
PandaDoc leans heavily into visibility:
- tracking begins at document creation, with changes logged in an audit trail
- analytics can show how stakeholders interact with each page (useful for deal coaching)
For revenue leadership, this is the difference between “sent a proposal” and “can coach the team based on what buyers actually read.”
PandaDoc5) Content library (reusable, governed building blocks)
A content library is positioned as a centralized repository for approved assets—snippets, images, layouts, and templates—so teams don’t recreate content from scratch.
Best practice: Treat the content library like a “single source of truth” for:
- legal clauses
- compliance disclosures
- approved product descriptions
- customer proof blocks (case studies, testimonials)
This reduces compliance risk and increases speed.
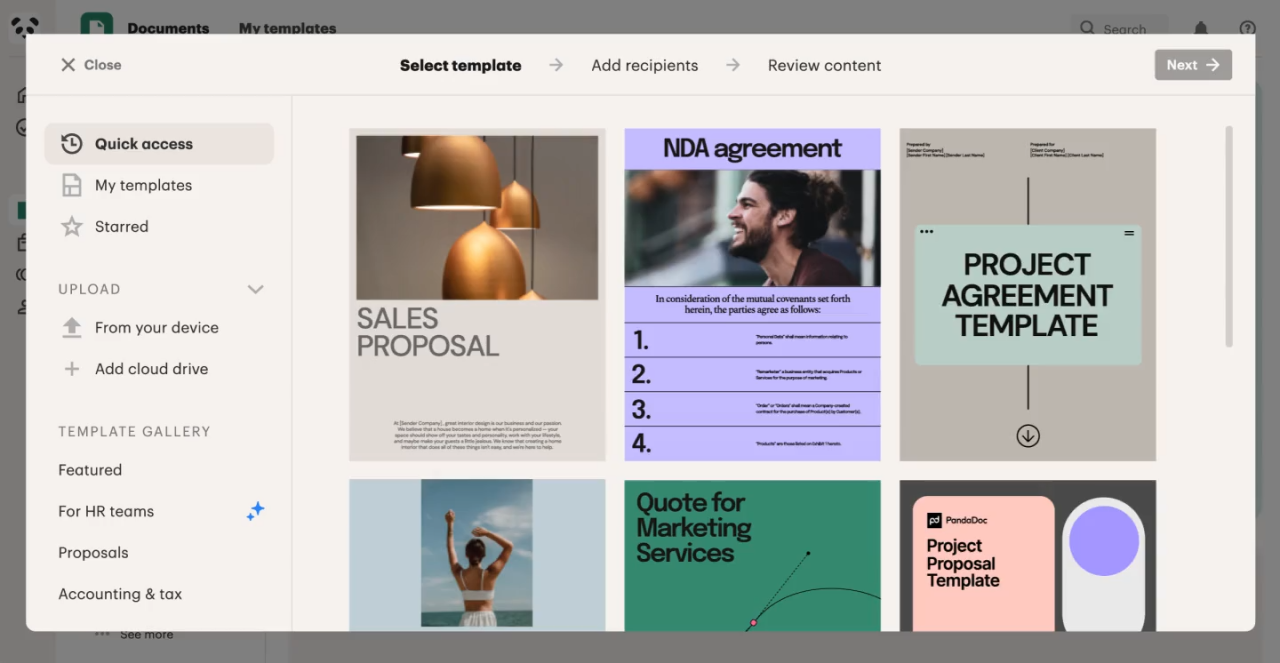
6) Pricing tables and product catalog
For sales-led organizations, quoting is where deals get messy—especially when pricing changes frequently or discounting rules are inconsistent.
PandaDoc includes:
- pricing tables to present line items, quantities, and totals
- a product catalog that acts as a repository for sellable inventory and can serve as a “source of truth” during quoting
PandaDoc’s help center flags pricing tables as a Business/Enterprise capability, which is important for plan selection.
7) Bulk send
Bulk send is designed for high-volume outbound workflows (HR documents, renewals, standardized agreements). PandaDoc describes bulk sending as:
- distributing documents/emails to multiple recipients at once
- requiring a template with dynamic content blocks and a CSV file with recipient data
Where it shines:
- seasonal contract updates
- policy acknowledgements
- multi-client renewals
What to watch: Bulk send amplifies errors. Template governance and variable testing become critical.
8) Approval workflows
Approval workflows are essential for preventing “bad deals” from reaching customers. PandaDoc describes approval workflows as:
- assigning approvers at the template level
- setting approval order to define who reviews at each stage
If your organization has discount bands, non-standard terms, or regulated requirements, approval workflows are typically the feature that turns document tooling into process tooling.
9) Rooms (deal rooms / shared workspace with buyers)
Rooms are positioned as a personalized deal room to organize resources, collaborate, negotiate, and complete deals in one place.
This directly addresses a common modern sales challenge: buyers don’t want 17 attachments and 30 emails. They want a single place to review, share internally, and execute.
Advanced Features and Integrations
1) PandaDoc AI Contract Assistant (AI document management)
PandaDoc highlights an AI assistant model where users:
- ask questions about contract terms
- get instant summaries
- track engagement
- automatically organize files via conversational interaction
It also explicitly mentions AI-generated email copy for sending contracts, proposals, and follow-ups.
Where AI is genuinely valuable
- first-pass contract summaries for non-legal stakeholders
- rapid extraction of commercial terms (renewal dates, discounts)
- helping reps write consistent, on-brand follow-up messaging
Where you still need humans
- anything requiring legal interpretation or risk acceptance
- edge cases in negotiated agreements
2) CPQ (Configure, Price, Quote)
PandaDoc CPQ focuses on:
- pricing rules and dynamic calculations
- bundling and pre-defined rulesets
- approvals triggered by thresholds
- two-way CRM synchronization (HubSpot and Salesforce highlighted)
If your quotes are complex (modular offerings, upsells, contract duration pricing, regional pricing), CPQ is where PandaDoc can justify its platform approach.
PandaDoc3) Workflow automations
PandaDoc positions workflow automation as:
- syncing with CRMs
- scheduling follow-ups based on document status
- automated reminders and collaboration triggers
It even outlines a simple setup approach: “Create automation,” choose an action (move doc to folder/cloud storage, send doc when status updated), and inherit automation settings via templates.
4) API, webhooks, and embedding
For technical teams, PandaDoc’s developer tooling is a major asset:
- API endpoints for document creation (POST /public/v1/documents)
- webhooks to notify your systems when document status changes
- embedded signing with a TypeScript library and region support (com/eu)
- “recipes” guidance for embedding signing flows and expected engineering effort
Who should care about this:
- SaaS platforms embedding signatures into their product
- marketplaces or partner ecosystems needing in-app contracts
- RevOps teams building advanced automation beyond native integrations
5) Integrations ecosystem (and what’s worth connecting)
PandaDoc emphasizes embedded integrations with CRMs like HubSpot, Salesforce, and Pipedrive to pull accurate customer data into documents.
It also supports broad integration coverage through Zapier (Zapier’s page notes connectivity to thousands of apps).
Top integrations table (practical shortlist)
| Category | Integrations you’ll likely use | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| CRM | HubSpot, Salesforce, Pipedrive | Prefill templates, sync deal context, reduce manual copy/paste |
| Payments | Stripe, PayPal, Square, Authorize.net, QuickBooks Payments | Convert “signed” into “paid” inside the same workflow |
| Collaboration | Slack, Microsoft Teams | Route notifications and keep deal momentum visible |
| Automation | Zapier | Fill integration gaps quickly, trigger workflows across tools |
| Productivity | Microsoft Word, Google Sheets (Zapier connector) | Bridge structured data and document output |
How seamless are integrations?
For CRM-first orgs, the best sign is that PandaDoc promotes “embedded integrations” (not just webhook glue). The more you can keep users in their core system (CRM), the better adoption tends to be.
Performance, Reliability, and Security
Reliability and uptime visibility
PandaDoc operates a public status page with component-level reporting across:
- creating/editing documents
- sending/opening
- uploading/downloading
- integrations
- API and webhooks
- web and mobile applications
- separate US/Global and EU service views
This matters because it gives customers a way to distinguish “our network is down” from “vendor incident” quickly.
Security posture (high-level)
PandaDoc states:
- compliance with E‑SIGN and UETA for US signature validity requirements
- commitment to HIPAA compliance and safeguards for handling ePHI workflows
- SOC 2 backing (referenced in its security materials)
Security controls and operational practices
PandaDoc’s security documentation references:
- least privilege employee access
- isolated environments for production vs other segments
- 24/7/365 monitoring and on-call escalation
- layered uptime techniques (auto-scaling, load balancing, rolling deployments) and daily encrypted backups
Data residency and subprocessors
PandaDoc offers a choice of data center locations (US or EU). However, it also notes meaningful operational constraints:
- communications with support may be global
- integrations enabled by customers can transfer data outside the chosen region
- no direct transfer between data centers; separate accounts may be required
PandaDoc also maintains a public list of subprocessors used to deliver services and describes due diligence expectations for third parties.
Authentication and signing artifacts
- 2FA is supported, with documented constraints for Google OAuth/SSO sign-ins (2FA must be handled at the identity provider in those cases).
- Signature certificates are available for completed documents and appear on the last page of downloaded PDFs (useful for audit and legal workflows).
Customer Support and Resources
PandaDoc’s ecosystem includes:
- Help Center documentation
- learning academy and webinars
- contact and onboarding services
- premium support options (called out in navigation/resources)
Its status page also directs users to the help center or to submit a request within the PandaDoc application for urgent issues.
What this implies: PandaDoc is built to support both self-serve adoption and high-touch enterprise deployment—good news if you anticipate cross-functional rollout.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
User Reviews and Ratings Summary
On PandaDoc’s pricing page, the company displays aggregated marketplace ratings:
| Marketplace | Rating shown |
|---|---|
| G2 | 4.7/5 (3,082 reviews) |
| Capterra | 4.5/5 (1,077 reviews) |
| GetApp | 4.5/5 (1,077 reviews) |
Common praise themes (what users tend to value)
Based on typical patterns for platforms in this category—and aligned with PandaDoc’s product emphasis—praise often clusters around:
- template-driven speed (less rework, faster sending)
- a modern buyer experience (interactive docs, tracking)
- visibility into engagement and pipeline execution
Common complaint themes (what to watch in adoption)
Most “all-in-one” workflow tools face similar friction points:
- setup complexity when you go beyond templates into CPQ/approvals/automation
- governance decisions (who owns templates, catalogs, approvals)
- training needs for cross-functional adoption
PandaDoc’s breadth is a strength—but only if you implement it intentionally.
Trends over time
PandaDoc continues to ship notable capabilities in areas like compliance and AI workflows, according to its product updates communications.
Alternatives and Comparisons
Here are four common alternatives, each with a distinct “center of gravity.”
Top alternatives
1) DocuSign (signature-first, enterprise standard)
DocuSign is often the default for enterprise eSign, with pricing examples including: Standard: $25/user/month billed annually, with envelope limits (100 per user/year noted on the pricing page).
Choose DocuSign if: signature compliance and enterprise procurement standardization matter more than proposal/quote workflows.
2) Dropbox Sign (HelloSign) (simple eSign + good UX)
Dropbox Sign pricing shows: Essentials: $15/month; Standard: $25/user/month (with annual billing options). Dropbox help center also notes a free tier includes 3 document transactions per month.
Choose Dropbox Sign if: you want lighter weight signing and straightforward templates.
3) Adobe Acrobat / Acrobat Sign (PDF-first productivity suite)
Adobe’s business pricing pages emphasize Acrobat as an all-in-one PDF + e-sign solution: Acrobat Standard for teams: $14.99/seat/month (annual, billed monthly); Acrobat Pro for teams: $23.99/seat/month (annual, billed monthly).
Choose Adobe if: your workflow is heavily PDF-centric and you want editing + signing in one Adobe ecosystem.
4) Proposify (proposal-first)
Proposify pricing lists: Basic: $19/user/month annually (or $29 monthly); Team: $41/user/month annually; Business: starts at $3,900 annually including 5 users.
Choose Proposify if: your primary need is proposals and sales docs, and you can rely on another tool for signatures or deeper agreement management.
PandaDocSide-by-side comparison table
| Tool | Best at | Starting price (published) | When it beats PandaDoc |
|---|---|---|---|
| PandaDoc | End-to-end document workflow: create → quote → collaborate → sign → track | Free tier + paid seats (Starter/Business) | When you need the full workflow in one platform |
| DocuSign | Enterprise eSign standardization | $25/user/mo (annual) for Standard | If eSign compliance + enterprise standardization is the only priority |
| Dropbox Sign | Lightweight eSign simplicity | $15/mo Essentials; $25/user/mo Standard | If you want minimal workflow overhead |
| Adobe Acrobat | PDF creation/editing + signing | $14.99–$23.99/seat/mo (annual billed monthly) | If PDF editing is the heart of your workflow |
| Proposify | Proposal creation and sales collateral | $19/user/mo annually (Basic) | If proposal design is the core requirement |
Who Is PandaDoc Best For (And Who Should Avoid It)
Best for
- Revenue teams (Sales + RevOps) that need quoting consistency, discount governance, and CRM-connected workflows
- Organizations with repeatable document pipelines (proposals, MSAs, renewals, onboarding documents) using templates + tracking + audit trails
- Teams that want buyer experience differentiation using Rooms and interactive content rather than attachment sprawl
- Product and platform teams embedding signing or document workflows via API/webhooks
Consider avoiding if
- You only need simple eSign with minimal workflow
- Your legal workflow is fully Word-native and you want zero change (PandaDoc can support negotiation, but adoption may still require process shifts)
- You operate in multi-region environments where data residency requirements could force account duplication and operational complexity
Final Verdict and Recommendations
Overall rating: 8.8/10
Rating breakdown (8.8/10 overall)
- Core features: 9.2/10 (document generation, tracking, auditability, templates)
- Advanced workflow: 9.0/10 (CPQ, approvals, automation, Rooms)
- Integrations & extensibility: 8.8/10 (CRM focus + Zapier + API + embedded signing)
- Security & compliance: 9.0/10 (E‑SIGN/UETA, HIPAA posture, data residency options, SOC2 references)
- Value for money: 8.2/10 (strong value at Business; add-ons like QES credits can surprise)
- Ease of adoption: 8.1/10 (excellent for template-driven teams; steeper for CPQ + governance rollouts)
Recommendation
- If you’re a template-driven sales org that wants measurable, repeatable deal execution, PandaDoc is a top-tier choice.
- If you’re a RevOps-led org dealing with quoting complexity and wanting CRM-embedded workflows, PandaDoc CPQ is particularly compelling.
- If you only need signatures, evaluate lighter tools first—otherwise you risk paying for workflow power you won’t implement.
Next step: run a structured trial: build 3 templates, connect your CRM, configure one approval rule, and measure cycle time and close rate impact over 2–3 weeks. PandaDoc promotes a 14‑day trial path that aligns with that approach.
PandaDoc
PandaDoc is a great addition to any business with its many features and flexibility. PandaDoc is basically a web-based application that allows users to create, deliver, and share documents online and place their legally binding signatures for faster paperless transactions and processes. The system supports various document forms including PDFs, Docs, and other pre-existing digital documents. It works well with quotes, contracts, agreements, and other sales collateral. There has been a 15% increase in average contract value with PandaDoc, one hour saved per week per employee and a 10% increase in close rate. PandaDoc is the future of document managing.…

FAQ (15 common questions)
1) Is PandaDoc free?
Yes—PandaDoc offers a Free eSign tier with 60 documents per year and unlimited seats, which works for low-volume signing.
2) What’s the best PandaDoc plan for small businesses?
Most small businesses outgrow “Free” quickly due to the document cap. Starter is usually the entry point for real sales workflows, while Business is better if you need templates + governance + quote tooling.
3) Does PandaDoc replace DocuSign?
It can, depending on your needs. If you want eSign plus document creation, tracking, and quote workflows in one tool, PandaDoc may replace signature-only tooling. DocuSign remains a common choice for enterprise-standard eSign procurement.
4) Does PandaDoc support legally binding signatures?
PandaDoc positions its eSignature software as compliant with U.S. E‑SIGN and UETA requirements and provides audit artifacts like signature certificates.
5) What’s the difference between audit trail and signature certificate?
Audit trail: detailed history of status changes and activity during the document lifecycle.
Signature certificate: a certificate appended to the completed PDF showing signing context and evidence.
6) Can PandaDoc show whether someone read my proposal?
Yes—PandaDoc markets tracking and analytics, including insights into how stakeholders interact with each page of proposals and contracts.
7) Does PandaDoc have CPQ?
Yes. PandaDoc CPQ supports rules-based pricing, bundles/rulesets, approvals, and CRM-based quoting workflows.
8) Does PandaDoc integrate with HubSpot and Salesforce?
Yes—PandaDoc emphasizes embedded CRM integrations with tools like HubSpot and Salesforce to import accurate customer data into documents.
9) Can PandaDoc collect payments?
PandaDoc highlights payment workflows through integrations (e.g., Stripe, PayPal) and notes it uses external processors rather than storing payment card data.
10) What are PandaDoc Rooms?
Rooms are a “deal room” concept: a centralized digital workspace to organize resources, collaborate, negotiate, and complete deals.
11) Does PandaDoc support workflow automation?
Yes—PandaDoc describes document workflow automation and outlines how to create automations tied to template-driven workflows.
12) Does PandaDoc offer an API?
Yes—PandaDoc provides a public API for document generation, plus webhooks for status updates, and embedded signing options for in-app experiences.
13) Can I embed signing into my own app?
Yes—PandaDoc provides embedded signing documentation and tooling (including a TypeScript library and region support).
14) Does PandaDoc support EU Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)?
Yes—PandaDoc supports QES and documents requirements and pricing, including a $5 per unique signer credit model.
15) Can I choose where my data is stored?
PandaDoc offers data residency options (US or EU), but notes limitations such as not being able to transfer data between data centers and the need for separate accounts to maintain regional separation.





By clicking Sign In with Social Media, you agree to let PAT RESEARCH store, use and/or disclose your Social Media profile and email address in accordance with the PAT RESEARCH Privacy Policy and agree to the Terms of Use.